Colon Cancer
Colon Cancer
Colon Cancer: Symptoms and Causes
Colon cancer is one of the most common types of cancer worldwide. It falls under gastrointestinal cancers and is also known as bowel cancer or malignant colon tumors. Its danger lies in the fact that it can begin silently, without clear symptoms, which makes early detection vital for improving the chances of recovery. In this article, we’ll cover the most important information about this disease—from symptoms and causes to diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.

What is Colon Cancer?
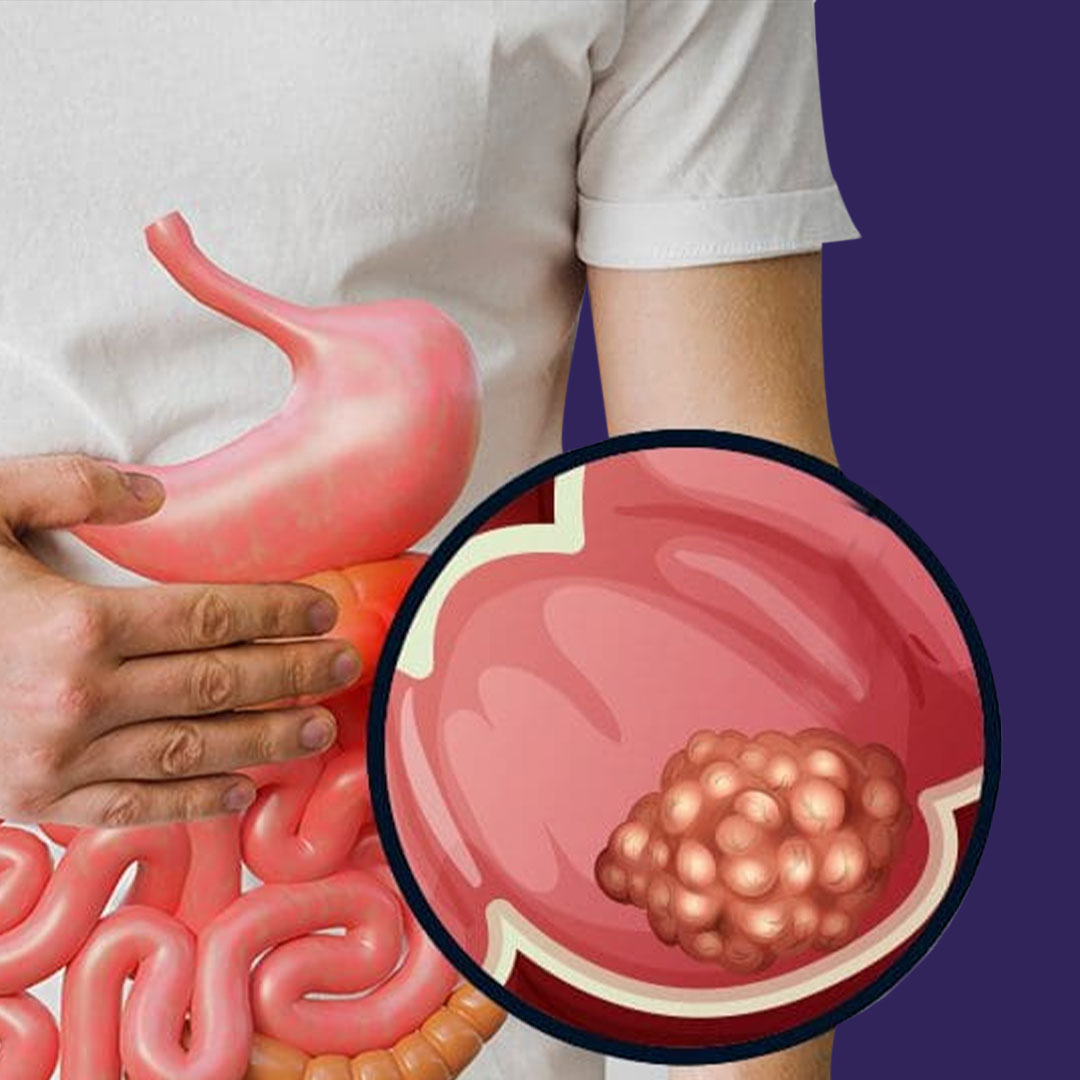
Colon cancer is the abnormal growth of cells in the lining of the colon or rectum, which are parts of the large intestine. It often begins with the formation of colon polyps, which are small benign growths that may, over time, develop into malignant tumors. Not all polyps are cancerous, but some can become cancerous if not detected and removed early.
Symptoms of Colon Cancer
The symptoms of colon cancer vary depending on the stage of the disease, and there may be no symptoms in the early stages. As the disease progresses, warning signs begin to appear, such as:
- Rectal bleeding or blood in the stool.
What is the color of blood in colon cancer?
It is usually dark red or mixed with the stool and can sometimes appear black if the bleeding is from the upper part of the colon.
- Changes in bowel habits such as prolonged diarrhea or constipation.
- A feeling of incomplete bowel emptying.
- Persistent abdominal pain or cramps.
- Unexplained weight loss.
- Chronic fatigue and general weakness.
Where is colon cancer pain located?
Pain is often concentrated in the lower abdomen, especially on the left or right side depending on the tumor’s location.
When do colon cancer symptoms appear?
Symptoms typically appear after the cancer has developed for some time, usually in relatively advanced stages. That’s why regular checkups and colonoscopies are critically important for early detection.
Causes and Risk Factors of Colon Cancer
There is no single specific cause of colon cancer, but several factors can increase the risk, including:
- Age:
Risk increases after the age of 50.
- Family history:
Having first-degree relatives with colon cancer.
- Chronic intestinal diseases :
- Diet high in red meat and low in fiber.
- Lack of physical activity.
- Obesity.
- Smoking and alcohol consumption.
Types of Colon Cancer
There are various types of colon cancer, but the most common is:
- Adenocarcinoma:
Accounts for over 95% of cases and originates from glandular cells in the colon lining.
Less common types include:
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- Mucinous Adenocarcinoma
- Small Cell Carcinoma
Stages of Colon Cancer
Colon cancer is divided into four main stages:
- First Stage :
The tumor is limited to the inner layer of the colon wall.
- Second Stage :
The tumor spreads to the muscular wall or nearby tissues but not to the lymph nodes.
- Third Stage :
The cancer spreads to one or more lymph nodes.
- Fourth Stage :
The cancer spreads to other organs such as the liver or lungs.
The earlier the cancer is detected, the higher the chances of successful treatment with available therapies.
Diagnostic Tests for Colon Cancer
Diagnosis relies on a combination of procedures and tests, including:
- Colonoscopy:
The most important and accurate test for diagnosing colon polyps and detecting cancer.
- Fecal occult blood test:
Detects invisible blood in the stool.
- Blood tests:
Including iron level tests and the "CEA" test, which is a tumor marker.
- CT scans and MRI Used to determine the extent of tumor spread.
Treatment of Colon Cancer
Treatment depends on the stage of the cancer, the patient’s condition, and the tumor type. Options include:
- Surgery:
The first option for early-stage colon tumors.
Involves removing the affected part of the colon along with nearby lymph nodes.
- Chemotherapy:
Used after surgery in some cases or when the disease has spread.
Helps shrink the tumor and prevent recurrence.
- Radiation therapy:
Mostly used for rectal cancer rather than colon cancer.
- Targeted therapy:
Targets specific molecules in cancer cells and is used in some advanced cases.
Preventing Colon Cancer
The risk of colon cancer can be reduced by adopting a healthy lifestyle and undergoing regular screenings. Preventive measures include:
- Regular colonoscopies after the age of 50 or as recommended by a doctor.
- A diet rich in fiber, fruits, and vegetables while reducing processed and red meat intake.
- Regular physical activity.
- Maintaining a healthy weight.
- Avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol.
- Managing chronic intestinal conditions like ulcerative colitis.