Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative Colitis
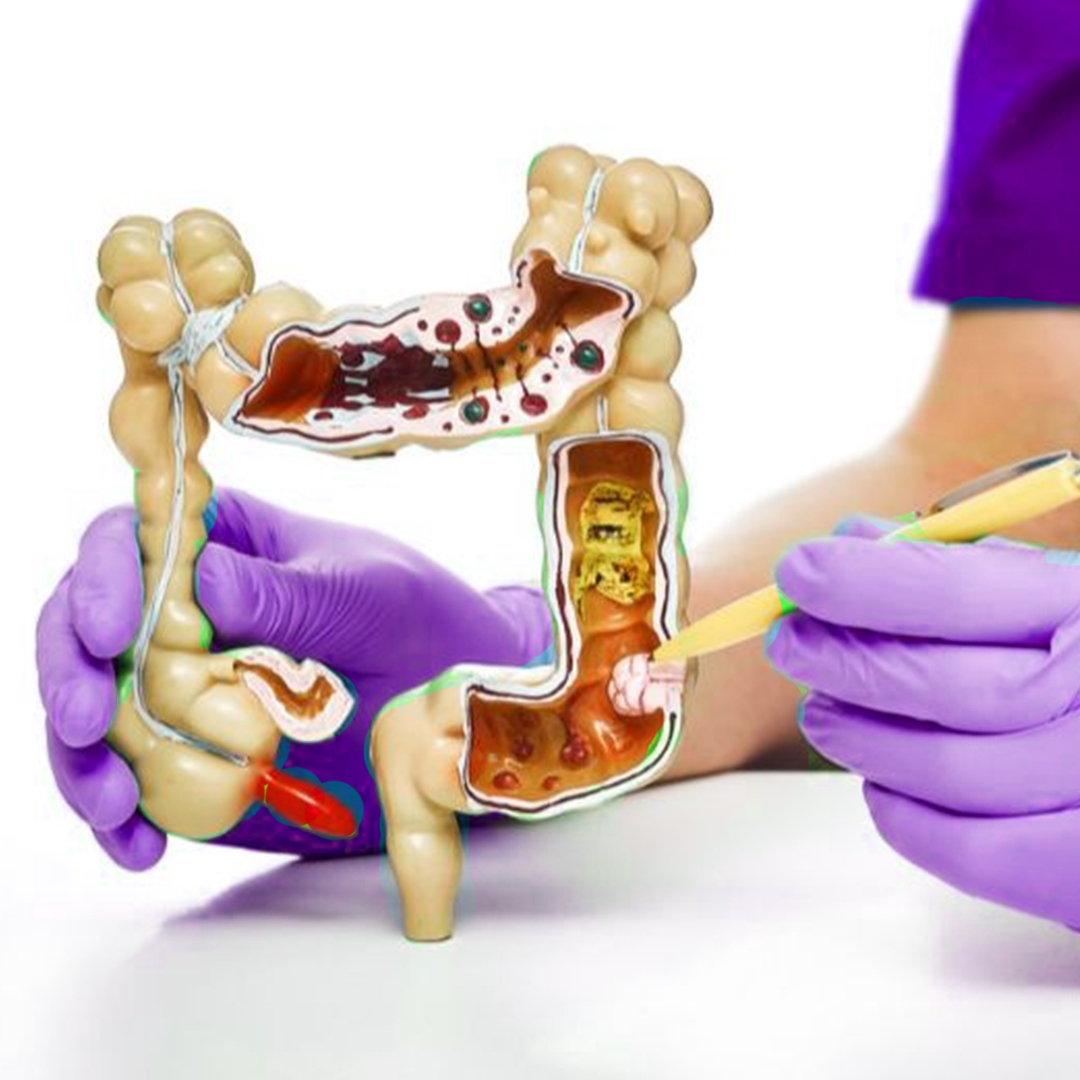
Ulcerative Colitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Ulcerative colitis is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease that affects the colon and rectum. It is one of the major types of inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), causing ulcers and pain in the digestive tract. In this article, we will cover all aspects of ulcerative colitis, from its causes and symptoms to treatments and prevention.

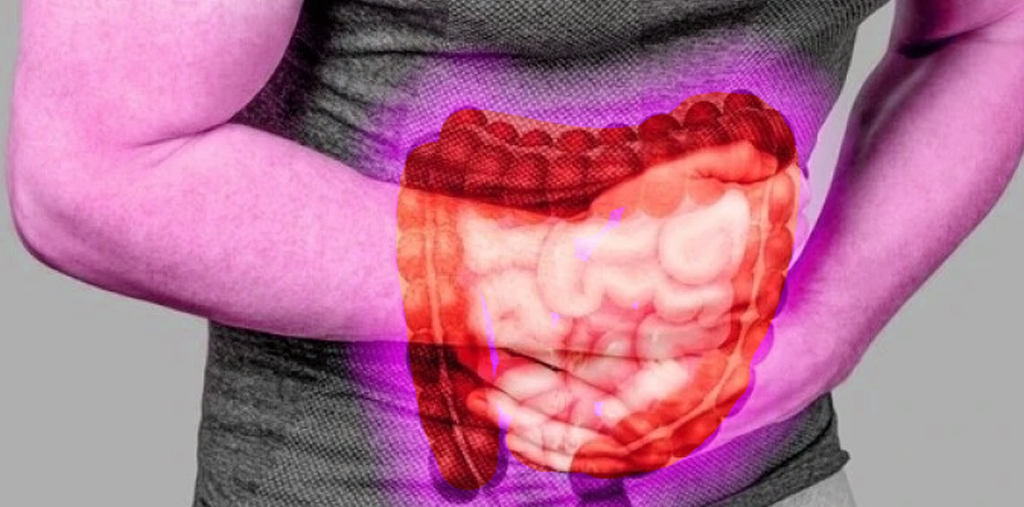
What is Ulcerative Colitis?
Ulcerative colitis is a chronic medical condition that causes inflammation and ulcers in the lining of the colon and rectum. It is a form of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). The inflammation typically begins in the rectum and gradually extends to other parts of the colon. Ulcerative colitis differs from other gastrointestinal diseases in that the ulcers form in the surface layer of the intestinal wall.
Ulcerative Colitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Causes of Ulcerative Colitis
The exact cause of ulcerative colitis is not known, but several factors may contribute to its development:
- Genetic factors:
A family history of ulcerative colitis increases the likelihood of developing the condition.
- Immune system:
Sometimes, the immune system attacks healthy cells in the colon and rectum, causing inflammation and ulcers.
- Environmental factors:
Environmental factors such as diet and infections may play a role in the development of the disease.
Symptoms of Ulcerative Colitis
Symptoms vary depending on the severity of the disease, but they typically include:
- Abdominal pain and cramping
- Chronic diarrhea, which may contain blood or mucus
- Weight loss and general fatigue
- Fever and loss of appetite
- Fever and loss of appetite
Treatment for Ulcerative Colitis
Treatment for ulcerative colitis includes medications to reduce inflammation and manage symptoms:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs:
Such as medications containing 5-aminosalicylates.
- Immunosuppressive drugs:
Such as corticosteroids that reduce acute inflammation.
- Biological therapy:
In advanced cases, biological drugs may be used to treat inflammation.
- Surgery:
In severe cases, colon removal may be necessary.
Risk Factors for Ulcerative Colitis
Risk factors that may lead to the development of ulcerative colitis include:
- Family history:
Having family members with the disease increases the risk.
- Age:
The disease typically appears during adolescence or early adulthood.
- Smoking:
Smoking is thought to increase the risk of developing the disease.
Complications of Ulcerative Colitis
If not properly managed, ulcerative colitis can lead to several complications, such as:
- Colon cancer:
People with long-term ulcerative colitis may be at increased risk of colon cancer.
- Toxic megacolon:
A severe complication that can occur in cases of acute inflammation, leading to tissue damage.
- Intestinal obstruction:
Chronic inflammation can cause narrowing of the colon.
Diagnosis of Ulcerative Colitis at Dr. Mohamed El-kady's Center for Gastroenterology and Endoscopy
- Medical history and physical examination:
To determine symptoms and accompanying signs.
- Colonoscopy:
To directly examine the colon and observe ulcers.
- Blood tests:
To check for inflammation or anemia.
- X-rays:
To assess the extent of the disease’s effect on the colon.
Treatment for Ulcerative Colitis
The treatment varies depending on the severity of the disease, and can be summarized as:
- Medications:
Including anti-inflammatory drugs like salicylates and biological drugs for advanced cases.
- Dietary changes:
Avoiding foods that may trigger inflammation, such as fatty or spicy foods.
- Surgery:
In advanced cases, surgery may be required to remove parts of the colon or even the entire colon.
Can Ulcerative Colitis be Cured?
There is currently no permanent cure for ulcerative colitis, but symptoms can be well managed with appropriate medications and lifestyle changes. In some cases, surgery may be the final solution for advanced disease.
What is the Difference Between Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) and Ulcerative Colitis?
Although the symptoms of IBS and ulcerative colitis may sometimes overlap, there is a significant difference:
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS):
A functional disorder that does not cause inflammation or tissue damage.
- Ulcerative Colitis: