Mallory-Weiss Syndrome
Mallory-Weiss Syndrome
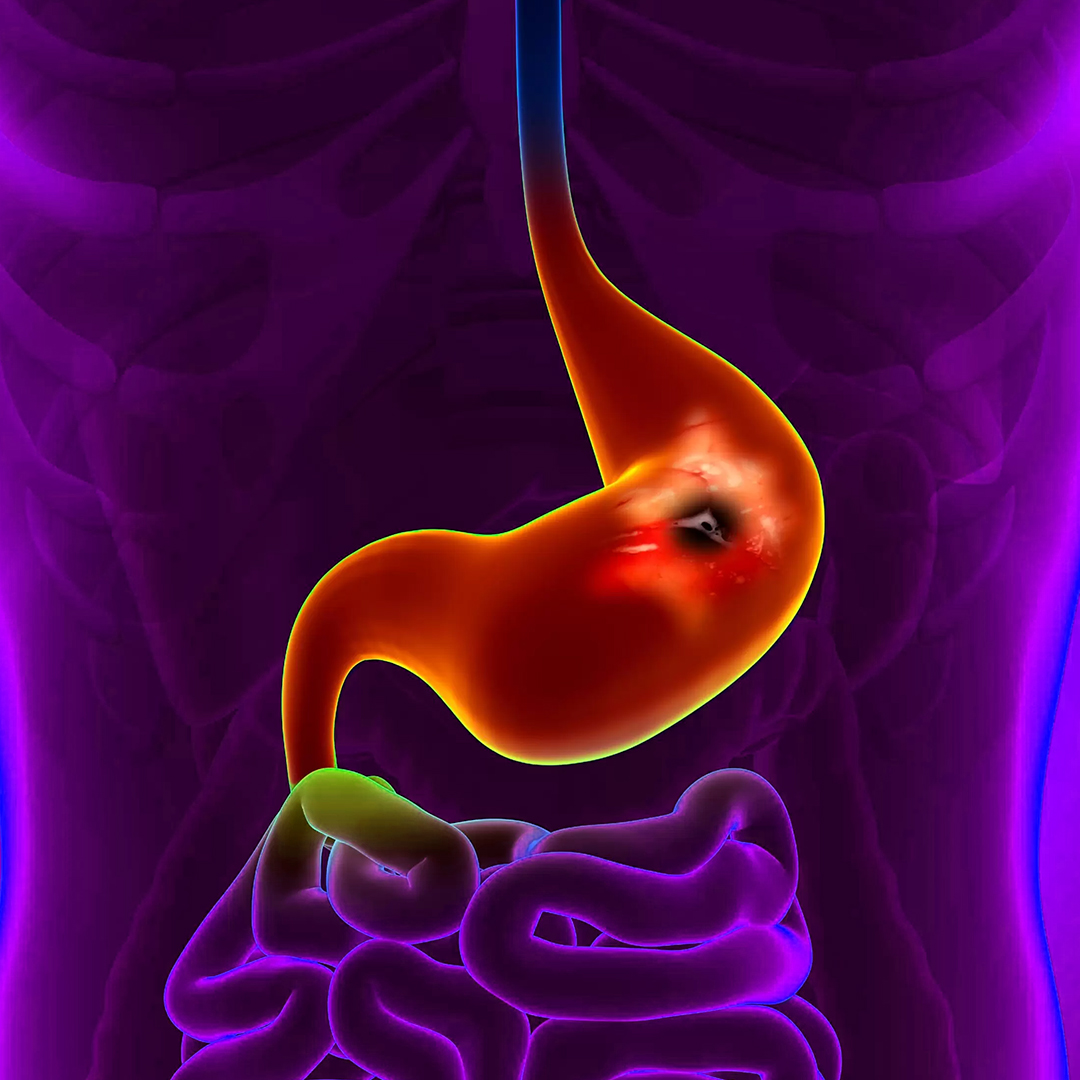
Mallory-Weiss Syndrome: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Methods
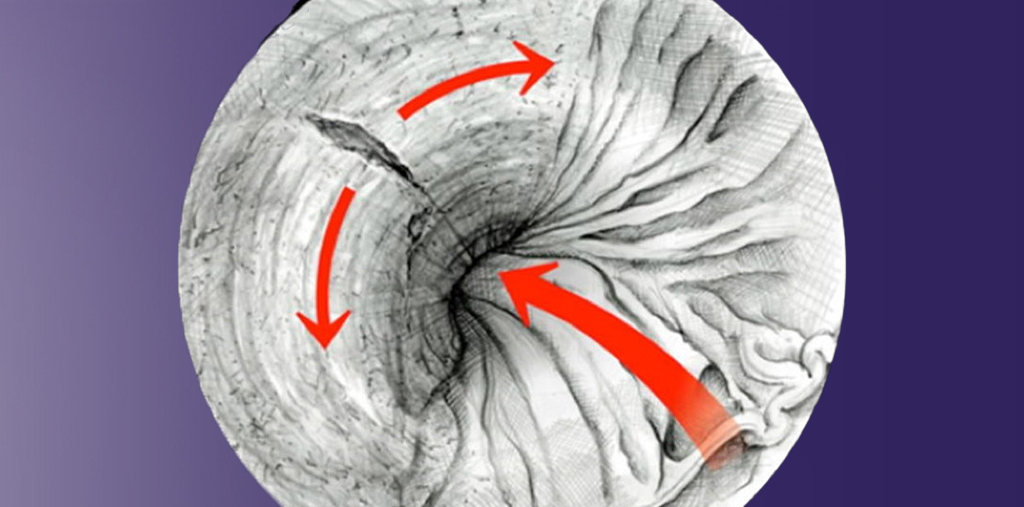
Mallory-Weiss syndrome is a medical condition characterized by a tear in the mucous membrane of the esophagus, usually occurring in the area between the esophagus and the stomach. This tear typically results from severe vomiting or persistent coughing, leading to internal bleeding in the upper gastrointestinal tract. The condition is named after the doctor who discovered it, "Mallory Weiss." It is considered a medical emergency as it can result in upper gastrointestinal bleeding, which can be life-threatening in some cases.

Causes of Mallory-Weiss Syndrome
The causes of Mallory-Weiss syndrome are related to excessive pressure exerted on the esophagus during severe vomiting or continuous coughing. This pressure can cause a tear in the mucous membrane of the esophagus between the esophagus and the stomach. The factors that may lead to Mallory-Weiss tears include:
- Severe vomiting:
Excessive vomiting, caused by conditions such as alcohol poisoning or digestive disorders, is a major cause of this syndrome.
- Excessive alcohol consumption:
Alcohol irritates the mucous membrane of the esophagus, increasing the likelihood of this condition.
- Physical strain:
Such as persistent coughing or lifting heavy weights that put pressure on the esophagus.
Symptoms of Mallory-Weiss Syndrome
The main symptoms of Mallory-Weiss syndrome include:
- Upper gastrointestinal bleeding:
This is usually the primary symptom observed in patients.
- Chest pain:
A sharp or pressure-like pain in the chest can be a sign of the tear occurring.
- Hematemesis:
Patients may experience vomiting of blood as a result of internal bleeding.
- Weakness and dizziness:
Due to blood loss, the patient may feel generally weak or dizzy.
Factors That Increase the Risk of Mallory-Weiss Syndrome
Several factors can increase the likelihood of developing Mallory-Weiss syndrome:
- Excessive alcohol consumption:
Drinking large amounts of alcohol is one of the most common causes of tears in the esophageal mucous membrane.
- Digestive health conditions:
Such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or peptic ulcers.
- Frequent vomiting:
Whether due to medical conditions or food poisoning.
- Neurological or psychological disorders:
Such as eating disorders that cause forced vomiting.
Complications of Mallory-Weiss Syndrome
If Mallory-Weiss tears are not treated appropriately, the condition can lead to serious complications such as:
- Hemorrhagic shock:
Due to severe bleeding.
- Infection:
Prolonged bleeding can lead to infections in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Esophageal stricture:
In rare cases, the tear can cause narrowing of the esophagus, which affects the ability to swallow food properly.
Prevention Tips from Dr. Mohamed Al-kady, Gastroenterologist and Endoscopist
Preventing Mallory-Weiss syndrome involves following a few tips that can help reduce the risk:
- Treat digestive disorders:
Such as managing GERD or reducing stress that may lead to continuous vomiting.
- Avoid forced vomiting:
Prevent situations that may lead to forced vomiting, such as certain eating disorders or food poisoning.
- Monitor blood pressure:
High blood pressure can increase the risk of injury to the esophagus.
Treatment for Mallory-Weiss Syndrome with Dr. Mohamed Al-kady, Gastroenterologist and Endoscopist
Treatment varies depending on the severity of the condition, and it includes:
- Medications:
Drugs are used to reduce bleeding and promote healing of the tears, such as acid-suppressing medications.
- Surgical intervention:
In cases of severe bleeding, surgical intervention may be necessary to repair the tear and stop the bleeding.
- Fluid therapy:
Intravenous fluids are given to compensate for blood loss and stabilize the patient's condition.
- Supportive care: