Liver cancer
Liver cancer
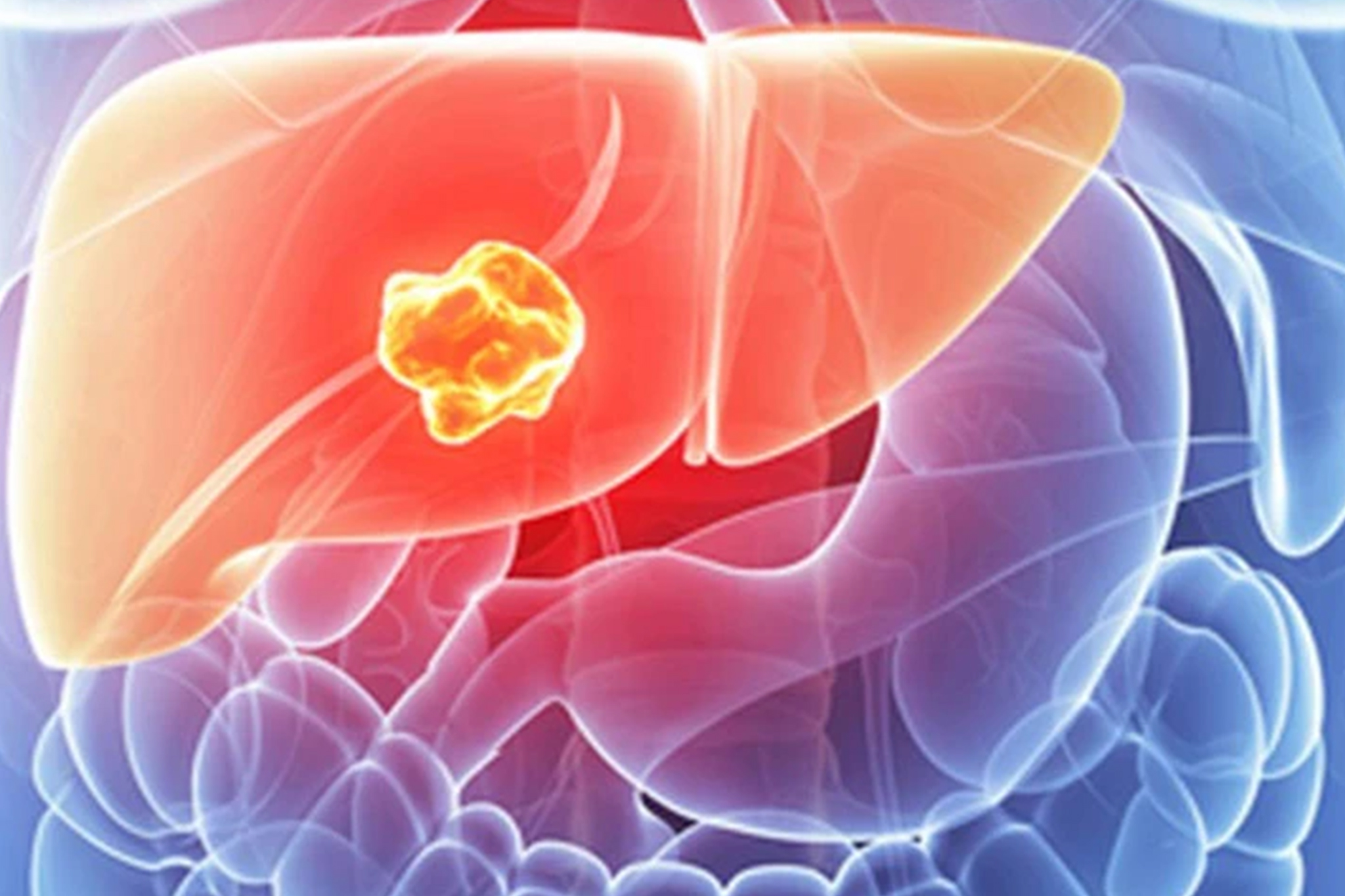
What is Liver Cancer?
Liver cancer is a type of malignant tumor that affects the liver cells. Hepatocellular carcinoma is the most common type of liver cancer. It develops when liver cells undergo abnormal changes and start growing uncontrollably, leading to the formation of tumors in this area. A person may have primary liver cancer, which originates in the liver itself, or it can be a result of cancer spreading from other areas of the body.

Types of Liver Cancer
There are two main types of liver cancer:
- Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC):
This is the most common type, originating in liver cells.
- Cholangiocarcinoma:
A less common type that begins in the bile ducts within the liver.
A person may also develop secondary liver cancer (advanced), which occurs when cancer spreads from other organs to the liver.
Symptoms of Liver Cancer
The symptoms of liver cancer vary depending on the stage of the disease. Common symptoms include:
- Liver swelling:
A person with liver cancer may feel a bloating or swelling in the upper right part of the abdomen.
- Abdominal pain:
The patient may experience severe pain due to pressure on surrounding tissues.
- Sudden weight loss:
Noticeable weight loss may occur.
- Jaundice:
Yellowing of the skin and eyes due to elevated bilirubin levels in the blood.
- General fatigue and weakness:
Constant fatigue and low energy levels are common.
Stages of Liver Cancer
Liver cancer is usually classified into several stages based on the size of the tumor and the extent of its spread. The stages are:
- Stage 1:
The tumor is small and confined to the liver.
- Stage 2:
The tumor is larger or there are multiple tumors, but still confined to the liver.
- Stage 3:
The cancer has spread to large blood vessels in the liver or to nearby lymph nodes.
- Stage 4:
The cancer has spread to other organs in the body.
Causes of Liver Cancer
The development of liver cancer can be attributed to several potential causes, including:
- Hepatitis viruses:
Hepatitis B and C viruses are major causes of liver cancer. Chronic hepatitis can cause liver cell destruction over time.
- Fatty liver disease:
Accumulation of excess fat in the liver can lead to chronic inflammation and increased risk of cirrhosis, raising the risk of cancer.
- Genetic liver diseases:
Conditions like Wilson's disease, which causes copper accumulation in the liver, increase the likelihood of developing cancer.
- Aflatoxin poisoning:
Toxins produced by certain fungi that grow on agricultural crops like peanuts.
- Cirrhosis:
Cirrhosis caused by chronic liver inflammation increases the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Risk Factors for Liver Cancer
Several factors may increase the risk of developing liver cancer, including:
- Infection with hepatitis B or C viruses.
- Family history of genetic liver diseases.
- Excessive alcohol consumption that leads to liver cell destruction.
- Obesity and fat accumulation in the liver.
- Continuous exposure to aflatoxins.
- Cirrhosis caused by chronic liver diseases.
Complications of Liver Cancer
Liver cancer can lead to several severe complications, such as:
- Liver Failure:
Where the liver is no longer able to perform its vital functions.
- Internal bleeding:
Due to the dilation of blood vessels in the liver.
- Jaundice:
Caused by elevated bilirubin levels in the blood due to liver cell damage.
Diagnosis of Liver Cancer
The diagnosis of liver cancer requires several medical tests, such as:
- Physical examination:
The doctor checks for any unusual signs in the abdomen.
- Blood tests:
The doctor checks for any unusual signs in the abdomen.
- rays or MRI scans:
To detect tumors.
- Biopsy:
A sample of liver tissue is taken for microscopic analysis.
Treatment of Liver Cancer by Dr. Mohamed El-kady, Gastroenterology and Endoscopy consultant
The treatment method depends on the stage of the cancer and the patient's overall health. Treatment options include:
- Surgery:
The treatment method depends on the stage of the cancer and the patient's overall health. Treatment options include:
- Chemotherapy:
Used to treat advanced stages of cancer.
- Radiation therapy:
Used to shrink tumors.
- Liver transplant:
In advanced cases where the damaged liver needs to be replaced.
- Targeted therapy:
Drugs that specifically target cancer cells.
Prevention of Liver Cancer
To protect yourself from liver cancer, you can follow some preventive measures, such as:
- Prevention of hepatitis B and C infection:
Through available vaccines.
- Reducing alcohol consumption.
- Avoiding aflatoxin poisoning.
- Maintaining a healthy weight and exercising.
- Monitoring the treatment of chronic liver diseases like cirrhosis.