Gastrointestinal Endoscopy
Gastrointestinal Endoscopy
Gastrointestinal Endoscopy
Gastrointestinal endoscopy is an important medical tool that helps doctors diagnose and treat many diseases related to the digestive system. In this article, we will discuss what gastrointestinal endoscopy is, reasons for its use, potential complications, how to prepare for it, and tips for coping after the procedure.
What is Gastrointestinal Endoscopy?
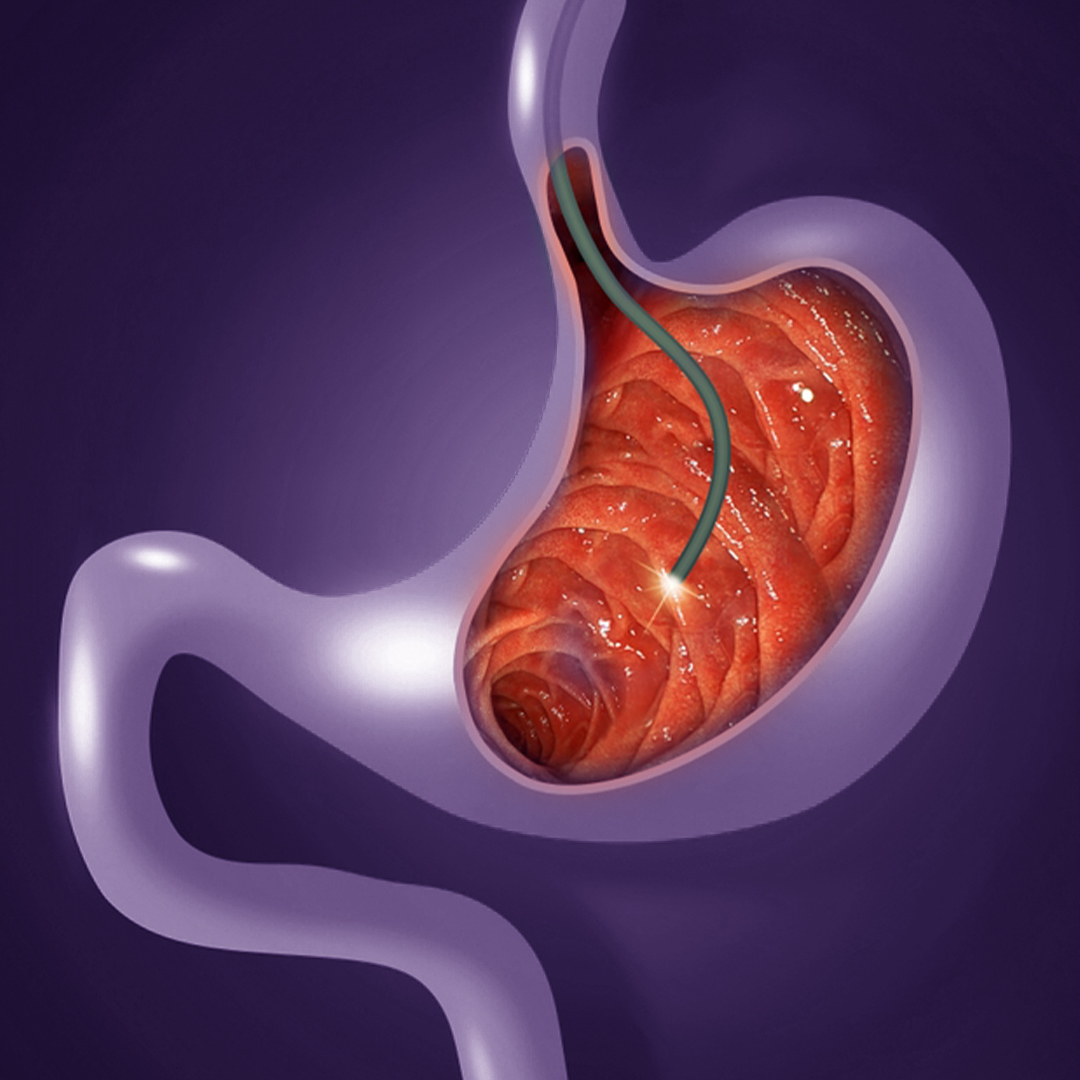
Gastrointestinal endoscopy is a medical device equipped with a camera and lights, used to examine and evaluate the internal parts of the digestive system, including the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine. The endoscope is inserted either through the mouth or the rectum, depending on the targeted area. Endoscopy is also used to perform some therapeutic procedures such as taking tissue samples (biopsies) or removing tumors.

Reasons for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy
There are several reasons that may necessitate gastrointestinal endoscopy, including:
- Unexplained Symptoms: Such as severe abdominal pain, persistent nausea, or unexplained weight loss.
- Diagnosis: To detect diseases such as ulcers, gastritis, tumors, or inflammatory conditions like Crohn’s disease.
- Treatment Monitoring: To monitor the condition of cancer patients or those with inflammatory bowel disease after treatment.
- Tissue Sampling: When there is suspicion of abnormal cells, to determine their nature.
Complications of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy
Although gastrointestinal endoscopy is generally a safe procedure, it may cause some complications, such as:
- Bleeding: Bleeding may occur after taking a biopsy or removing a tumor.
- Infection: There is a slight risk of infection.
- Bowel Perforation: This is a rare but serious condition where a hole may develop in the bowel wall during endoscope insertion.
- Reactions to Anesthesia: Some patients may experience adverse reactions to the sedative medications used.
How to Prepare for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy
Proper preparation for gastrointestinal endoscopy is crucial for ensuring the success of the procedure. Here are some tips for preparation:
- Fasting: Patients should refrain from eating and drinking for a specified period before the endoscopy, usually 6-8 hours.
- Medications: Patients should inform the doctor about all medications they are taking, as some may need dosage adjustments or to be stopped before the procedure.
- Avoiding Certain Foods: Patients may be advised to avoid heavy or fatty foods prior to the endoscopy.
Tips for Coping After Gastrointestinal Endoscopy
After undergoing gastrointestinal endoscopy, here are some tips for coping:
- Rest: It is important for patients to get adequate rest after the procedure.
- Avoid Strenuous Activities: Patients are advised to avoid heavy physical activities for a few days.
- Monitor Symptoms: Patients should keep an eye on any unusual symptoms such as severe pain or bleeding, and consult a doctor if they occur.
- Follow Medical Instructions: Adhere to the doctor’s instructions regarding diet and care post-procedure.
What Diseases Can Gastric Endoscopy Detect?
Gastric endoscopy can detect various diseases, such as:
- Gastritis
- Stomach ulcers
- Cancerous tumors
- Changes in tissue that indicate gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
Does Gastrointestinal Endoscopy Require Anesthesia?
Yes, gastrointestinal endoscopy typically requires anesthesia, whether general or local. The type of anesthesia is determined based on the patient’s condition and the duration of the procedure.
How Long Does Gastric Endoscopy Take?
Gastric endoscopy usually takes about 15 to 30 minutes, but the total time may include preparation and recovery periods.
Is Gastric Endoscopy Painful?
Patients may experience discomfort during the endoscopy, but the sedative medications used aim to minimize pain and anxiety. After the procedure, some may feel mild pain or bloating, but this is generally temporary.
Conclusion
Gastrointestinal endoscopy is an effective tool for diagnosing and treating many digestive system problems. By understanding the reasons for its use, potential complications, and the importance of good preparation, patients can navigate this procedure safely and benefit from its outcomes.
Read also: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment of Gastritis
