Gallstones
Gallstones

What are Gallstones?
Gallstones are solid deposits that form in the gallbladder, a small organ located beneath the liver that stores bile, which helps digest fats. Gallstones are made of substances like cholesterol or bilirubin and can vary in size, from very small to large. Their number can range from a single stone to multiple stones.

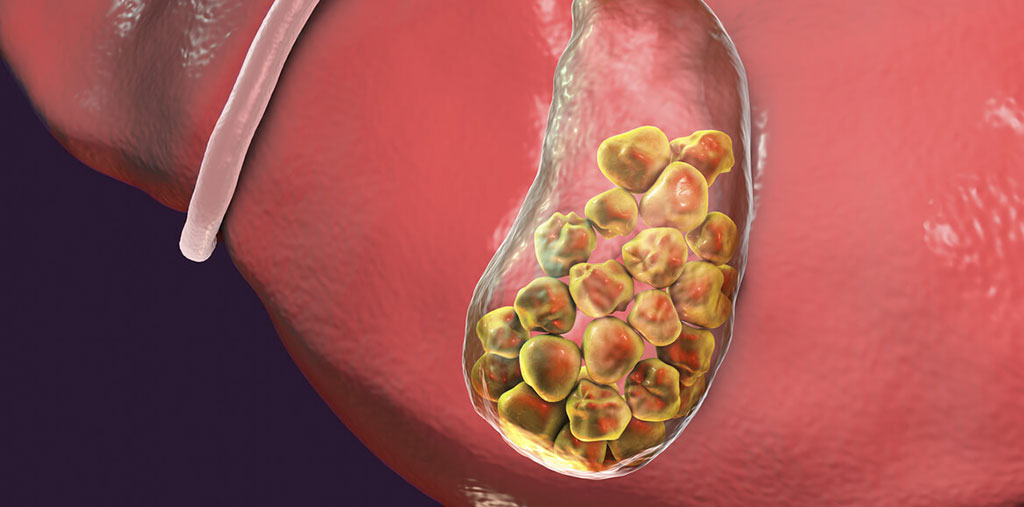
Types of Gallstones
Gallstones are classified into two main types:
- Cholesterol Stones:
These are the most common type and are formed due to an increase in cholesterol concentration in bile.
- Pigment Stones:
These stones form as a result of elevated bilirubin levels in bile, which can occur due to health issues like cystic fibrosis or hepatitis.
Causes of Gallstone Formation
There are several factors that contribute to the formation of gallstones, including:
- Increased Cholesterol in Bile:
This leads to the formation of cholesterol stones.
- Solid Deposits of Bile:
These may occur due to irregular bile flow.
- Disorders in Bile Composition:
Such as low bile concentration, which contributes to the formation of stones.
- Other Health Issues:
Conditions like diabetes or cystic fibrosis can increase the risk of developing gallstones.
Symptoms of Gallstones
In some cases, gallstones may not show any symptoms, and this is known as "silent gallstones." However, in other cases, patients may experience clear symptoms such as:
- Pain in the upper abdomen:
Especially after consuming fatty foods.
- Nausea and vomiting:
Due to the stones' effect on the digestive system.
- Jaundice:
The skin and eyes turn yellow due to the stones' impact on the bile ducts.
- Abdominal bloating:
This is also a common symptom with gallstones.
Complications of Gallstones
If gallstones are not treated appropriately, they can lead to serious complications, including:
- Cholecystitis:
Inflammation of the gallbladder, which can occur due to blockage of the bile ducts.
- Pancreatitis:
Inflammation of the pancreas caused by a blocked bile duct that is shared with the pancreas.
- Bile Duct Obstruction:
Leading to a buildup of bile in the body and the appearance of jaundice symptoms.
Factors That Increase the Risk of Gallstones
Several factors increase the likelihood of developing gallstones, including:
- Obesity:
Leads to higher cholesterol levels in the blood, thus promoting stone formation.
- Age:
The risk increases with age.
- Gender:
Women are more likely to develop gallstones than men.
- Genetics:
Family history may increase the risk of developing gallstones.
- Diet:
Eating large amounts of fatty foods can contribute to gallstone formation.
Diagnosis of Gallstones with Dr. Mohamed Elkady, Consultant of Gastroenterology and Endoscopy
Gallstones are usually diagnosed through a medical examination and the patient's health history. The diagnosis may include:
- Ultrasound (Sonography):
The most commonly used test to identify the presence of gallstones.
- Blood Tests:
To check for signs of inflammation or liver function issues.
- CT Scan or MRI:
In some cases, these scans can be used for more precise diagnosis.
Treatment of Gallstones with Dr. Mohamed Elkady
In some cases, gallstones may not require treatment if they are not causing symptoms. However, if they cause symptoms or complications, treatment becomes necessary. Treatment options include:
- Medications:
Some medications may help dissolve cholesterol stones over time, but this treatment can take a long period and may not be effective for large stones or if the stones have caused bile duct obstruction.
- Surgical Removal of the Gallbladder (Cholecystectomy):
This is the most common solution, where the gallbladder is surgically removed, permanently removing the stones.
- Laparoscopic Surgery:
In some cases, gallbladder removal is done using a minimally invasive laparoscopic technique, which results in a shorter recovery time.
Can Gallstones Be Treated Without Surgery?
Some individuals may be able to get rid of gallstones using medications that dissolve cholesterol stones. However, this takes time and may not be effective for large stones or if the stones have caused bile duct obstruction. In most cases, surgical removal remains the most effective treatment.
What Foods Should Gallstone Patients Avoid?
Gallstone patients should avoid foods that are high in saturated fats, such as:
- Fried foods
- Processed foods
- Full-fat dairy products