Esophageal Varices?
Esophageal Varices?
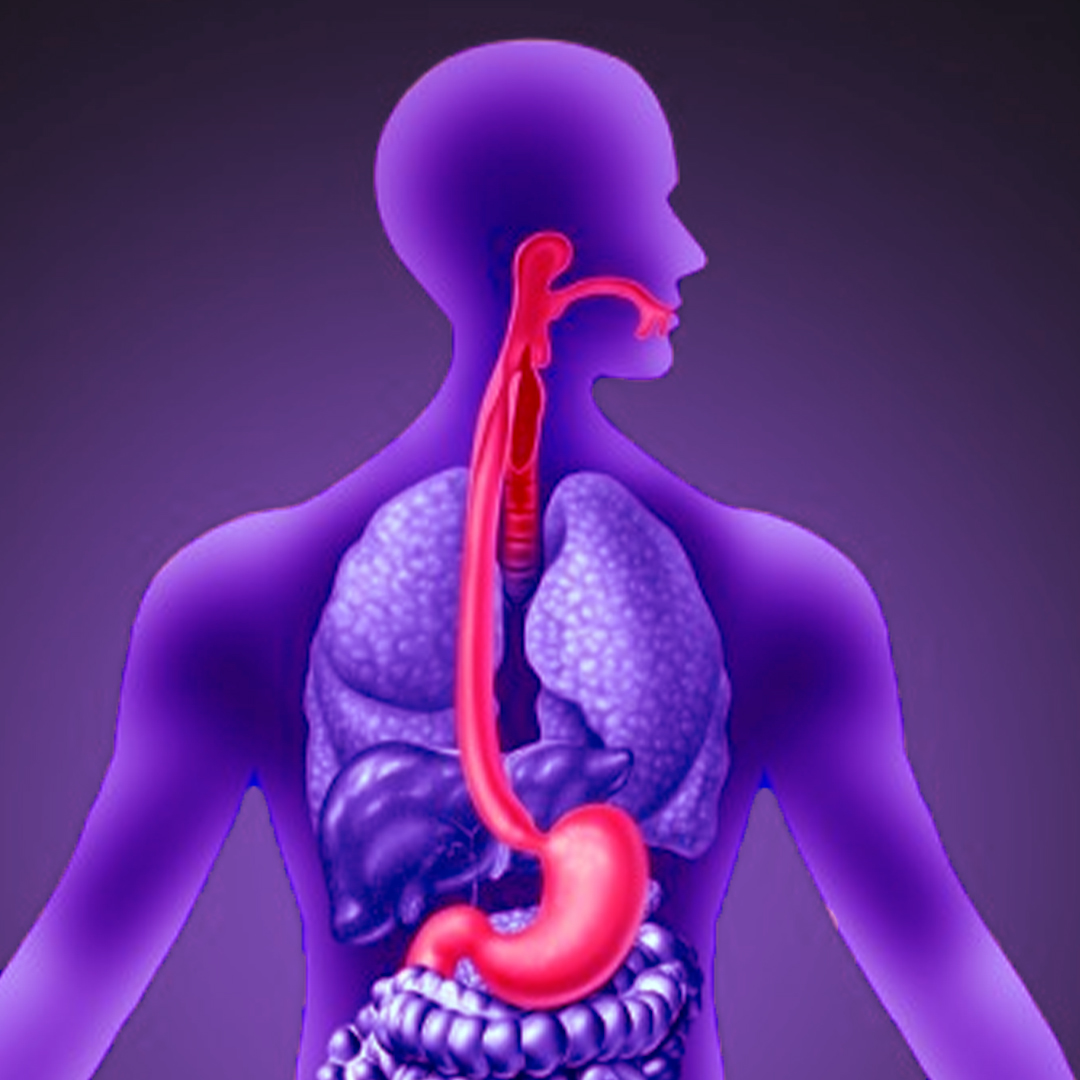
What is Esophageal Varices?
Esophageal varices is a medical condition that results in congestion of the blood vessels in the esophagus, the part that connects the mouth to the stomach. This congestion involves the expansion of veins in the esophagus, leading to the formation of what is known as esophageal varices. Esophageal varices are a symptom of portal hypertension (elevated blood pressure in the vein that carries blood from the digestive system to the liver), often caused by liver diseases such as cirrhosis. Esophageal varices can be dangerous if ruptured, as they may lead to severe bleeding in the esophagus.

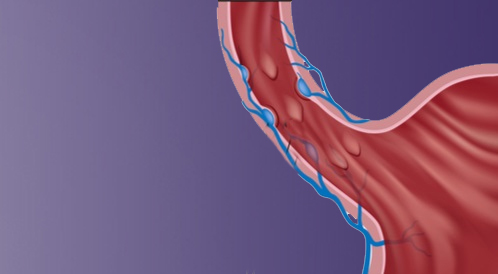
What are the Symptoms of Esophageal Varices?
The symptoms of esophageal varices may not be obvious initially, but as the condition progresses, some symptoms may appear, including:
- Esophageal Variceal Bleeding:
One of the most serious symptoms, it may appear as blood in the vomit or black stools.
- Chest pain:
The patient may experience pain or pressure in the chest due to the swelling and expansion of the veins.
- Difficulty Swallowing:
When the varices become large, they may affect the person's ability to swallow food easily.
- Dizziness or Fainting:
Due to blood loss or low blood pressure caused by bleeding.
Causes of Esophageal Varices
The causes of esophageal varices are multiple, with the condition often occurring due to portal hypertension caused by certain liver health issues. The main causes include:
- Cirrhosis:
The most common cause of portal hypertension, thus increasing the risk of developing esophageal varices.
- Other Liver Diseases:
Such as chronic hepatitis or cirrhosis caused by viral hepatitis.
- Blood Clots in the Portal Vein:
These may cause partial blockage in the vein, leading to portal hypertension.
Risk Factors that Increase the Chances of Developing Esophageal Varices
Several risk factors increase the likelihood of developing esophageal varices, including:
- Chronic Liver Disease:
People with conditions such as cirrhosis or viral hepatitis are more likely to develop esophageal varices.
- Excessive alcohol consumption:
Excessive alcohol consumption can severely damage the liver, increasing the chances of developing esophageal varices.
- Obesity:
Obesity can contribute to increased pressure on the liver and blood vessels.
- Portal Hypertension:
If a person suffers from portal hypertension, this increases the risk of developing esophageal varices.
Complications of Esophageal Varices
If esophageal varices are not treated properly, they may lead to serious complications such as:
- Acute Esophageal Variceal Bleeding:
This can result in significant blood loss, posing a life-threatening risk.
- Gastric and Esophageal Infections:
Continued bleeding may lead to infections in the digestive system.
- Liver Failure:
In advanced cases, cirrhosis may lead to liver failure, which exacerbates the development of esophageal varices.
Treatment of Esophageal Varices with Dr. Mohamed El kady , Consultant in Gastroenterology and Endoscopy
The treatment of esophageal varices depends on the severity of the condition and the presence of complications. With advances in medical technology, the treatment of esophageal varices has become more effective. The main treatment methods include:
- Endoscopic Treatment:
Endoscopy can be used to treat esophageal varices by stopping bleeding or banding the dilated veins using special bands or medical instruments. This is one of the most effective methods of treating esophageal varices.
- Medications:
Medications are used to lower blood pressure in the portal vein, such as vasodilators.
- Sclerotherapy:
In some cases, a chemical substance is used to shrink the dilated veins and prevent bleeding.
Dr. Mohamed El kady's Tips for Preventing Esophageal Varices
Esophageal varices can be prevented by following some guidelines that may help reduce risks, such as:
- Limit Alcohol Consumption:
Limit Alcohol Consumption:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight:
Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce pressure on the liver and digestive system.
- Adhere to a Healthy Diet:
A balanced diet helps maintain liver health and improve its function.
- Monitor Liver Health: