Crohn’s Disease
Crohn’s Disease
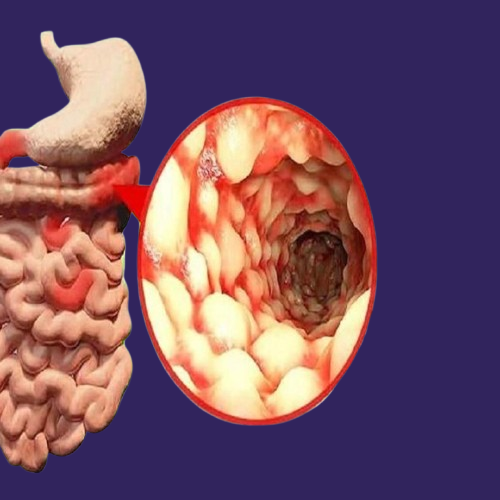
What is Crohn’s Disease?
Crohn’s disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), a chronic condition that affects the digestive system. It is characterized by inflammation in different parts of the digestive tract, from the mouth to the anus, but it most commonly affects the lower part of the small intestine and the first part of the colon. This inflammation can lead to ulcers and severe abdominal pain, and it may cause digestive issues, significantly impacting the lives of those affected by Crohn’s disease.

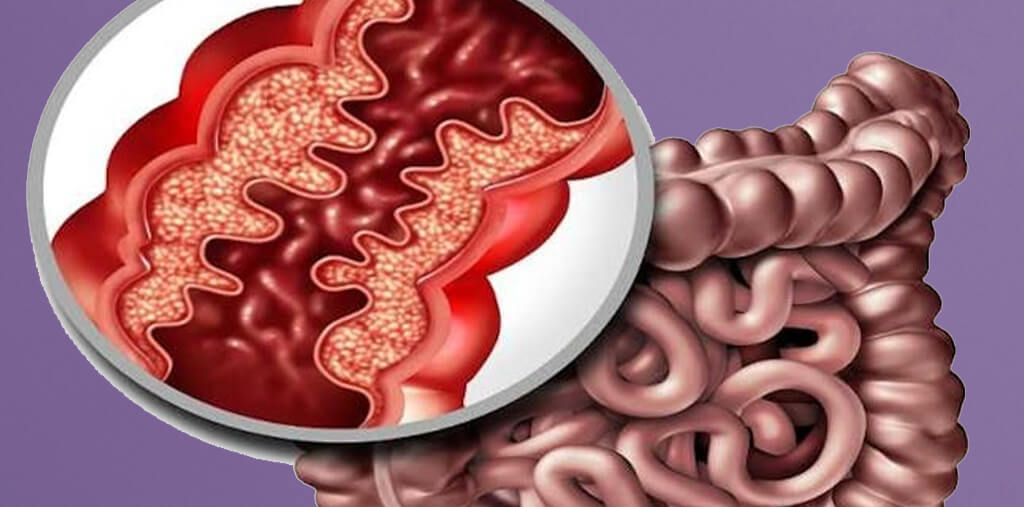
Types of Crohn’s Disease:
Crohn’s disease can affect any part of the digestive tract, and its severity varies. The main types include:
- Ascending Colon Crohn’s Disease:
which affects the small intestine and the ascending colon.
- Colonic Crohn’s Disease:
which affects the entire colon.
- Ileal Crohn’s Disease:
which affects the small intestine, particularly the ileum.
Causes of Crohn’s Disease:
There are no specific causes of Crohn’s disease, but it is believed that a combination of genetic, immune, and environmental factors may contribute to its development. People with a family history of inflammatory bowel disease are at a higher risk of developing the condition. Studies suggest that environmental factors such as smoking and infections may also act as triggers.
Risk Factors for Crohn’s Disease:
- Family History:
Having family members with Crohn’s disease increases the likelihood of developing the condition.
- Smoking:
Smoking is one of the risk factors that heighten the chances of developing the disease and exacerbating symptoms.
- Exposure to Certain Substances:
Environmental pollution or certain chemicals in food may play a role in developing Crohn’s disease.
Symptoms of Crohn’s Disease:
The symptoms of Crohn’s disease range from mild to severe and may include:
Diagnosis of indigestion with Dr. Mohamed El-Qadi
The doctor usually relies on the patient's medical history and the symptoms they complain of to diagnose indigestion. The doctor may request some tests such as:
- Abdominal pain:
Severe pain, especially in the lower abdomen.
- Diarrhea:
It may occur daily and sometimes be accompanied by mucus or blood.
- Weight loss:
Due to difficulty absorbing nutrients.
- General fatigue:
Caused by ongoing inflammation and nutrient loss.
Extra-intestinal Symptoms of Crohn’s Disease:
Some people with Crohn’s disease may experience symptoms not related to the digestive system, such as:
- Arthritis:
Joint pain and swelling.
- Skin and eye inflammation:
Skin rashes or eye inflammation may occur.
- Liver issues:
Such as hepatitis or bile duct problems.
Complications of Crohn’s Disease:
If Crohn’s disease is not treated properly, serious complications may arise, including:
- Bowel obstruction:
Due to scar tissue or inflammation in the intestines.
- Bowel perforations:
Ulcers can lead to holes in the intestines, causing infections.
- Cancer:
People with Crohn’s disease are at a higher risk of developing bowel cancer, especially after long-term disease.
How is Crohn’s Disease Diagnosed at Dr. Mohamed El-kady’s Gastroenterology and Endoscopy Clinic:
To diagnose Crohn’s disease, doctors use a variety of tests, including:
- X-rays or MRI imaging to observe the condition of the intestines.
- Endoscopy: To examine the intestines directly.
- Laboratory tests: Such as blood and stool tests to detect inflammation.
Treatment for Crohn’s Disease with Dr. Mohamed El-kady, Gastroenterology and Endoscopy Specialist:
Symptoms can be managed, and inflammation can be reduced with:
- Medications:
Such as anti-inflammatory drugs, immunosuppressive medications, and modern biological therapies.
- Surgery: