cholecystitis
cholecystitis
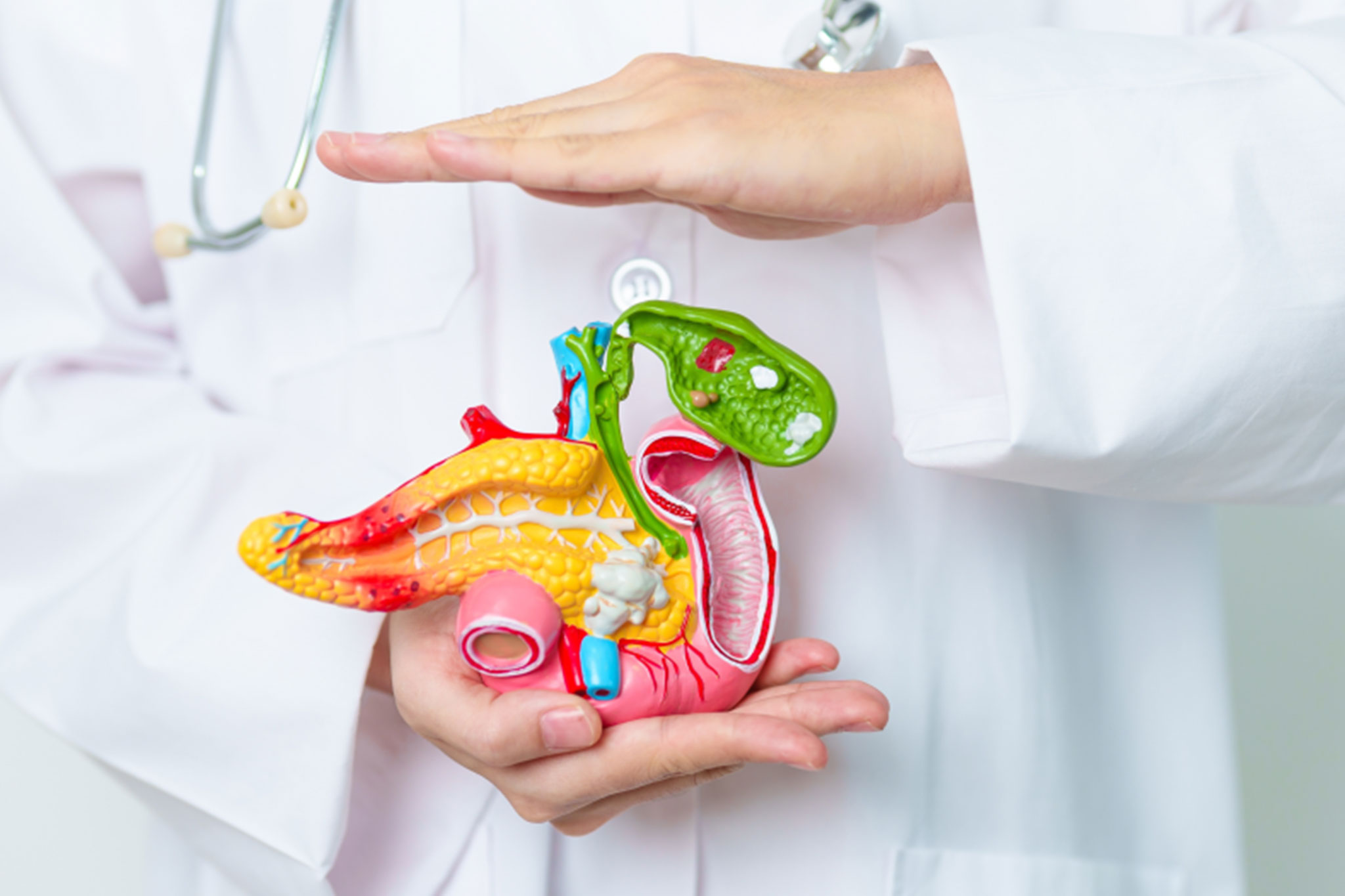
What is cholecystitis?
cholecystitis is a medical condition that occurs when the gallbladder, a small organ located beneath the liver that stores bile, becomes inflamed. This inflammation typically results from a blockage in the bile duct due to gallstones or bacterial infection. cholecystitis can cause severe pain in the upper abdomen and may lead to serious complications if not treated correctly.

Types of cholecystitis
- Acute cholecystitis:
This occurs suddenly and is characterized by severe abdominal pain, which may be accompanied by fever and nausea. It is often the result of a blockage in the bile duct caused by gallstones.
- Chronic cholecystitis:
Chronic cholecystitis:
Symptoms of cholecystitis
The symptoms of cholecystitis can vary from person to person, but common symptoms include:
- Sharp pain in the upper abdomen or the right side of the abdomen.
- Pain that may radiate to the back or the right shoulder.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Fever.
- A feeling of bloating or indigestion.
- A blockage in the bile duct due to gallstones may lead to more severe complications, such as a blocked bile duct or a ruptured gallbladder.
Causes of cholecystitis
The main causes of cholecystitis include:
- Gallstones:
Gallstones are the most common cause of cholecystitis. They can block the bile duct, causing bile to accumulate inside the gallbladder.
- Bacterial Infection:
An infection may occur in the gallbladder when bacteria enter through the bile duct.
- Bile Duct Blockage:
Bile Duct Blockage:
- Other Issues:
Occasionally, other conditions such as liver function disorders or digestive problems may contribute to cholecystitis.
Complications of cholecystitis
If left untreated, cholecystitis can lead to serious complications, including:
- Gallbladder Rupture:
If the inflammation becomes severe, the gallbladder wall may rupture, causing bile to leak into the abdominal cavity, which can lead to a generalized bacterial infection in the abdomen (peritonitis).
- Bile Duct Inflammation:
A blocked bile duct may become inflamed, causing severe pain and other health complications.
- Infection in the Gallbladder:
Infection can lead to tissue decay around the gallbladder.
- New Gallstones:
Recurrent gallbladder inflammation can lead to the formation of new gallstones.
Diagnosing cholecystitis
Doctors use a variety of tests to diagnose cholecystitis, including:
- Clinical examination:
A physical examination to assess symptoms such as pain and tenderness in the abdomen.
- X-rays or Ultrasound:
To detect the presence of gallstones or a blocked bile duct.
- Blood tests:
To detect the presence of gallstones or a blocked bile duct.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI):
In some cases, doctors may use advanced imaging techniques to determine the extent of the inflammation.
cholecystitis Treatment with Dr. Mohamed Al-kady, Gastroenterology and Endoscopy cosultant
Treatment options depend on the severity of the condition. Treatment includes:
- Medications:
Doctors may prescribe antibiotics for bacterial infections or pain relievers to alleviate symptoms.
- Gallbladder Removal:
In cases that cannot be treated with medication, gallbladder removal surgery (cholecystectomy) may be required. This surgery is typically successful and prevents further infections in the future.
- Gallstone Fragmentation:
In some cases, gallstones may be fragmented using sound waves or other techniques to remove the blockage in the bile duct.
Preventing cholecystitis
To protect yourself from gallbladder inflammation, it is recommended to follow some preventive guidelines:
- Eat a Healthy Diet:
Avoid fatty and fried foods, as they may increase the risk of developing gallstones.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight:
Obesity is a major risk factor for the development of gallstones.
- Exercise Regularly: