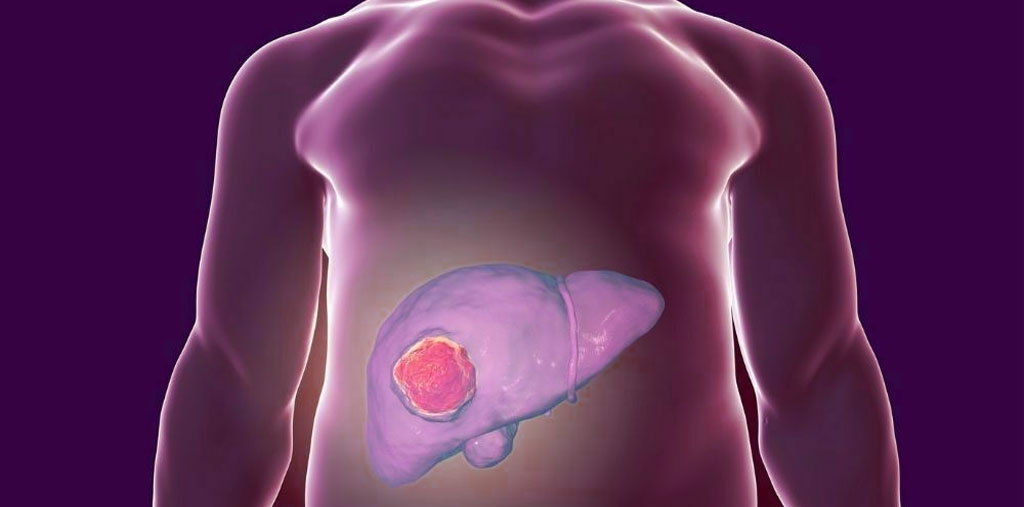
Hepatoblastoma
Hepatoblastoma
Treatment of Hepatoblastoma in Children
Hepatoblastoma is a rare type of cancer that affects the liver, and it can occur in children, especially. This tumor is considered a cancerous growth that affects liver cells and can lead to several severe health complications if not diagnosed and treated early. This article will cover everything related to hepatoblastoma in children, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, factors influencing treatment, and the latest treatment methods.

What is Hepatoblastoma?
Hepatoblastoma is a type of cancer that affects the liver and impacts liver cells. It is also known as "embryonal liver cancer" and usually occurs in children, particularly at a young age. Hepatoblastoma is characterized by abnormal growth of cells in the liver, which may lead to a significant decline in its function. It is one of the most common cancers in children, accounting for about 1% of all childhood cancers.
Causes of Hepatoblastoma
There is no specific cause for hepatoblastoma, but several factors may contribute to its development. These factors include:
- Hepatitis B Virus (HBV):
The hepatitis B virus may stimulate tumor growth in the liver and is considered one of the contributing factors to liver cancer development.
- Genetic Disorders:
Certain genetic disorders can increase the risk of developing this tumor, such as Niemann-Pick disease or Codon syndrome.
- Bile Duct Obstruction:
Bile duct obstruction in the liver, which occurs due to disorders leading to blockages in the bile ducts, may increase the risk of liver tumors.
Risk Factors That Increase the Chances of Developing Hepatoblastoma
Some factors may increase the likelihood of a child developing hepatoblastoma. These factors include:
- Genetic factors:
Children with certain genetic syndromes, such as Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome or Codon syndrome, are more likely to develop hepatoblastoma.
- Hepatitis Virus Infections:
As mentioned, the hepatitis B virus can increase the risk of liver cancer.
- Family History of Liver Cancer:
If a family member has had liver cancer, the child may be at a higher risk of developing it.
Symptoms of Hepatoblastoma
Symptoms vary depending on the size and location of the tumor, but the most common signs that may appear in children with hepatoblastoma include:
- Abdominal pain:
The child may experience persistent pain or cramps in the liver area.
- Abdominal Swelling:
The tumor may cause the liver to enlarge, resulting in noticeable abdominal swelling.
- Weight loss:
The child may lose weight unexpectedly due to the tumor's effect on the body.
- Jaundice:
The tumor may block the bile ducts, leading to yellowing of the skin and eyes.
- Nausea and Vomiting:
The child may experience constant nausea or vomiting due to pressure exerted by the tumor on surrounding organs.
Complications of Hepatoblastoma
If hepatoblastoma is not treated early, it can lead to several complications such as:
- Liver Failure:
Due to the destruction of liver cells, the child may suffer from chronic liver failure.
- Cancer Spread:
The tumor may spread to other organs such as the lungs or lymph nodes, complicating treatment.
- Sepsis:
Infection or inflammation due to the tumor or chemotherapy may lead to blood poisoning.
Diagnosis of Hepatoblastoma
To diagnose hepatoblastoma, doctors rely on a combination of tests and examinations, including:
- Clinical examination:
The doctor examines the child to check for symptoms such as abdominal swelling or jaundice.
- Imaging Tests:
rays, MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging), and CT (Computed Tomography) scans are used to determine the location and size of the tumor.
- Blood tests:
Tests may include liver function tests and measuring cancer markers in the blood.
- Liver biopsy:
The doctor may need to take a liver sample for microscopic analysis to confirm the tumor type.
Treatment of Hepatoblastoma
Treatment for hepatoblastoma varies based on factors such as tumor size, location, and the child's overall health. Treatment options include:
- Surgery:
If the tumor is operable, a surgical procedure may be performed to remove the tumor or the affected part of the liver.
- Chemotherapy:
If the tumor is operable, a surgical procedure may be performed to remove the tumor or the affected part of the liver.
- Radiation therapy:
Radiation therapy may be used in some cases to treat tumors that cannot be removed surgically or to shrink the tumor before surgery.
- Liver Transplantation: