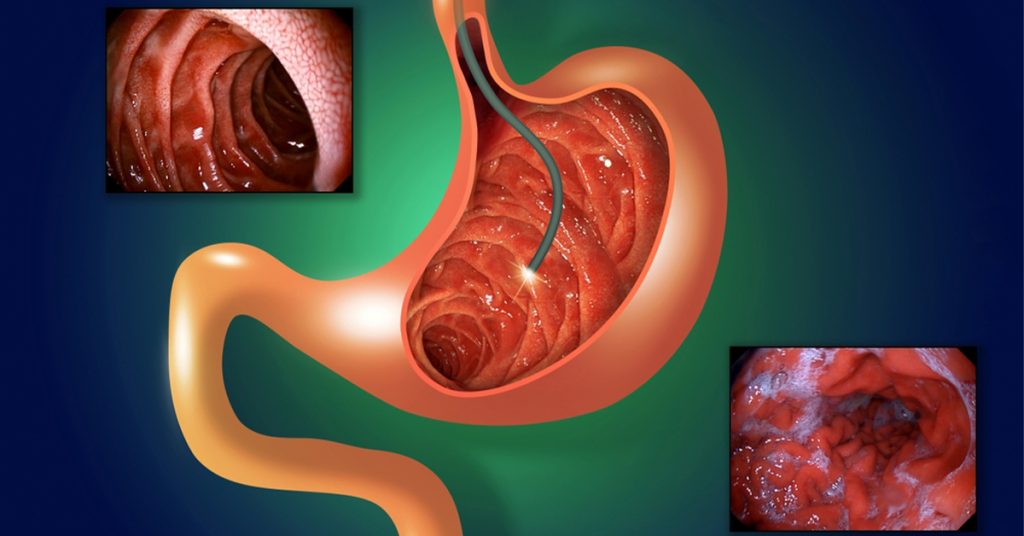
What is Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography?
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is a medical procedure used to diagnose and treat issues related to the bile ducts and pancreas. The primary aim of this procedure is to explore the bile ducts and identify any obstructions, stones, or tumors. This procedure is a valuable tool that allows doctors to have a direct view of the biliary system and take biopsies when necessary.
What Are the Reasons for Performing ERCP?
There are several reasons why doctors recommend performing an ERCP, including:
- Bile Duct Stones: The presence of stones can lead to blockage of the bile duct, causing severe pain.
- Pancreatitis: The procedure can help determine the underlying causes of pancreatitis.
- Tumors: Detection of tumors that may affect the bile ducts or pancreas.
- Liver Diseases: Using ERCP to evaluate various liver-related conditions.
How is ERCP Performed?
The procedure begins with the patient being sedated, either locally or completely. The endoscope is inserted through the mouth into the esophagus, then into the stomach and the small intestine. A special dye is then injected into the bile ducts, allowing for clearer imaging via X-rays. If stones are detected, special tools within the endoscope can be used to remove them without the need for surgery.
How to Prepare for ERCP
Preparing for the procedure requires some important steps:
- Fasting: Patients must refrain from eating or drinking for 6-8 hours before the procedure.
- Medical History: It’s important to inform the doctor about any medications being taken, especially blood thinners.
- Consultation: Discussing the potential risks and benefits of the procedure with the doctor is advisable.
Eating After ERCP
After the procedure, patients are advised to wait 6 to 12 hours before eating. After this period, they can start consuming light fluids such as water and broth, while avoiding fatty or heavy foods for 24 hours to minimize any discomfort.
Complications After ERCP
Although ERCP is generally considered safe, there are some potential complications, such as:
- Pancreatitis: This may occur after the procedure.
- Bleeding: In rare cases, bleeding can happen in the treated area.
- Infection: The procedure may lead to infections in the bile ducts.
Removing Bile Duct Stones via ERCP Without Surgery
Stones can be removed from the bile duct using specialized tools within the endoscope, allowing for treatment without the need for open surgery. This method is less invasive and helps alleviate symptoms quickly.
Is ERCP Painful?
Patients may experience some discomfort during the procedure, but pain is typically managed with effective analgesics. Many patients report the pain as mild and tolerable.
How Long Does ERCP Take?
The procedure usually takes between 30 to 60 minutes, although some more complex cases may require additional time. It is performed in a medical setting under the supervision of specialized doctors.
Is Blockage of the Bile Ducts Dangerous?
Blockage of the bile ducts can be dangerous if not treated, as it may lead to complications such as pancreatitis or infection. It is important to consult a doctor if any symptoms indicating a blockage occur, such as severe abdominal pain or jaundice.
Conclusion
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is an important medical procedure used to diagnose and treat conditions related to the bile ducts. This procedure requires careful preparation and an understanding of potential complications. If you are experiencing issues with your bile ducts, consulting your doctor about the benefits and methods of this procedure will be an important step toward improving your health.
